Authors: Sylviane de Viron, Data and Knowledge Manager
Nicolas Huet, Machine Learning Manager
Central monitoring helps sponsors proactively identify quality issues in clinical trials. To meet regulatory requirements, support continuous improvement, and enable further optimization of issue detection through machine learning, it is imperative to document the follow-up of central monitoring findings from initial detection through resolution. The documentation of risk follow-up activities should detail what was done to investigate the risk (and by whom), confirm whether an actual issue was identified and explain what was done to address the issue and/or secure its closure (1).
The Root Cause Decision Support feature, first released to the CluePoints Monitoring Platform in December 2021, aims at helping sponsors flag signals that may not be sufficiently documented. The feature alerts users when the documentation of a signal is unclear and encourages them to provide further insights about risk signal investigations and follow-up activities.
Using Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques and a Deep Learning solution, the feature interrogates signal comments, mitigation rationales, and root cause rationales to predict whether a signal is unclear (i.e., the signal is not sufficiently documented) or clear enough. When proper documentation is entered, the feature automatically detects if a signal is likely an issue or a non-issue.
Signal Documentation
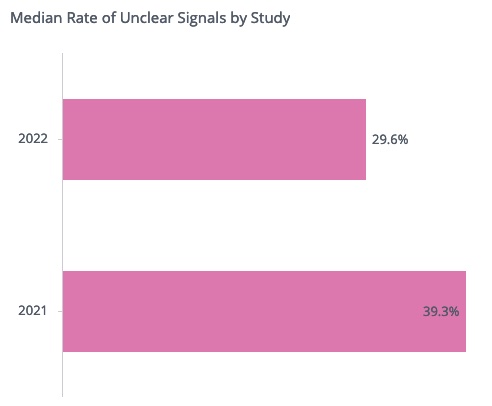
Since the feature release, we have seen a significant improvement in signal documentation. For example, out of all signals created in 2022 for which the sponsor already provided a root cause, in each study only 29.6% of the signals on average remained with unclear documentation. This is much lower than in 2021, when 39.3% of the signals per study on average had unclear documentation. This represents an overall reduction in unclear signals of about 25%.
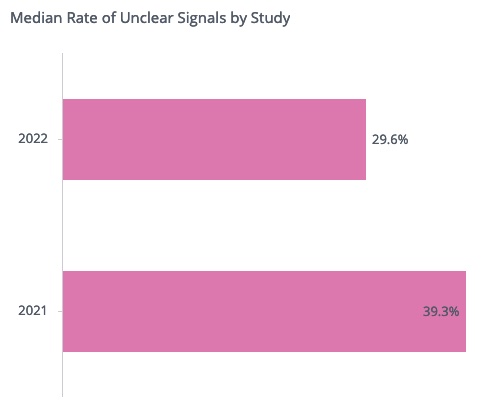
Interestingly, only 15.3% of the signals remain unclear to date in 2022 for organizations who started using the CluePoints platform within the past two years, which is significantly better than the overall observed rate of 29.6%. It is apparent that there is greater awareness of the importance of signal documentation among these organizations. For organizations using the platform longer than two years, we do still observe a positive impact of the Root Cause Decision Feature, as the rate of unclear signals dropped from 40.0% in 2021 to 30.0% in 2022. Further adoption of this feature – along with greater attention to signal documentation best practices – is key to further improving signal documentation rates in the future.
Conclusion
Our analysis provides clear evidence that NLP helps sponsors to improve their signal documentation. Further, the analysis shows that most organizations already benefitted from the Root Cause Decision Support feature in 2022. Therefore, we believe there should be a continuous follow-up of adopting the Root Cause Decision Support feature to assess how the metrics presented here will evolve. Our expectation is that signal documentation will keep benefiting from the Root Cause Decision Feature and continue to improve as users become more familiar with this new feature and as central monitoring teams develop greater awareness of the need for documenting the full story of each risk within the CluePoints platform.
Reference
1. US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. A Risk-Based Approach to Monitoring of Clinical Investigations Questions and Answers [Internet]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA; 2019 [cited 2021 Aug 20]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/risk-based-approach-monitoring-clinical-investigations-questions-and-answers